THE PROBLEM:
Issues with Standard Calibration Devices
Inaccurate results
There are over 12 sources of error associated with open neck and mechanical provers, leading to inaccurate calibrations.
Inefficient processes
Many calibration devices still require heavy human involvement. This slows down the process and creates the opportunity for human error.

The Solution:
Coriolis Reference Meter Prover (C.RMP)
C.RMP provides high quality on-site measurements for the calibration of retail fuel dispensers. Every step of the process is controlled by a computer software system to provide Electronic Calibration.
C.RMP uses the Coriolis Measurement Principle to evaluate flow rate and volume dispensed from a fuel dispenser. It gathers data on mass and density to calculate the two variables and then aggregates all of the information for reporting on our Site Quality Control (SQC) user interface. The data is then analyzed and compared to the individual client’s corporate standards. If the fuel dispenser is outside of the standards, the technician is notified that calibration is needed.
The highly automated process and closed loop nature of the system eliminates over 12 different sources of error that are present in standard calibration processes. The most substantial errors being human error (0.5%) and vapour loss (0.1-0.3%).
Benefits
Eliminate Human Error
Connect the C.RMP to the fuel dispenser and let the system do all of the work.
Improve Workflow
Speed up data entry and verification with highly automated processes.
Increase Operational Consistency
Capture each customer’s corporate standards in the system for consistent testing regardless of technician.
Detailed Client Reporting
Provide clients with detailed Dispenser Early Warning, Network Flow Rate Performance, Actionable Knowledge and Quarterly Calibration reports.
Improve Safety
Closed loop nature of the system prevents all harmful vapours from being released.
Accuracy
Accurate within ±0.05% of the flow rate being measured.
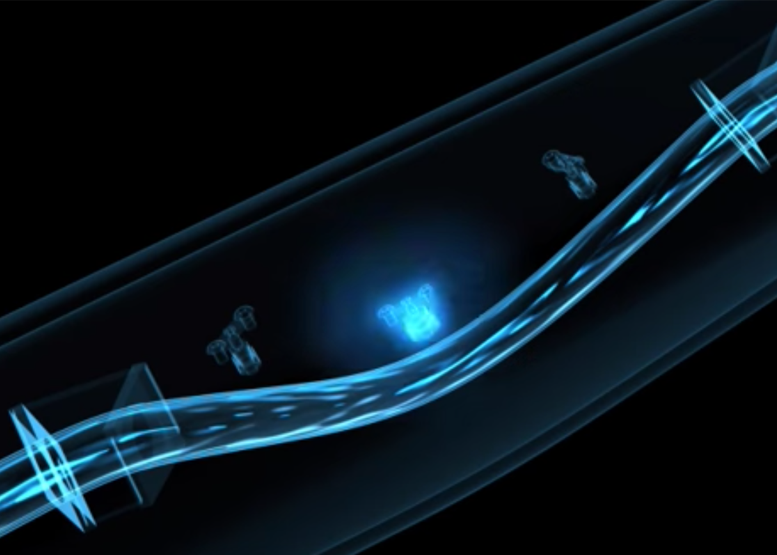
What is the Coriolis Measurement Principle?
For a detailed explanation of how the Coriolis force is utilized in a flow meter please watch the video to the left.
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial force that acts on objects that are in motion relative to a rotating reference frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motion of the object. In one with anticlockwise (or counterclockwise) rotation, the force acts to the right. Deflection of an object due to the Coriolis force is called the Coriolis effect.